- Ceramic: They are tiny, cheap, and fast, so they are used to remove noise in circuits. They do not care about direction (non-polarized), but they cannot store much energy.
- Electrolytic: They store a lot of energy, so they are used in power supplies. They have direction (+ and −), and connecting them wrong will damage them..
- film: They are tiny, cheap, and fast, so they are used to remove noise in circuits. They do not care about direction (non-polarized), but they cannot store much energy.
Capacitors
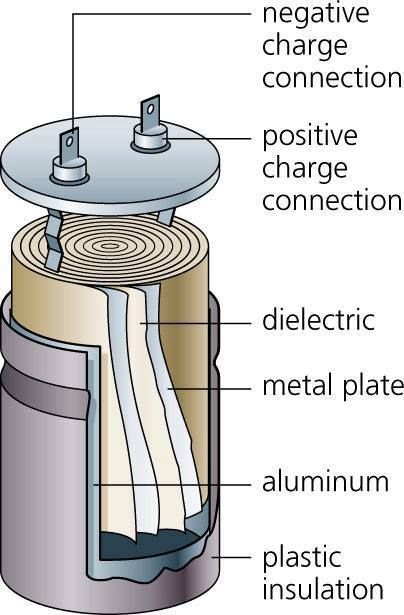
What is a Capacitor? AA capacitor is an electronic component that stores electrical energy in an electric field, functioning like a temporary, fast-recharging battery. It consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material called a dielectric. When a voltage is applied, the plates accumulate opposite electrical charges and can release them later when needed. Capacitors are widely used in electronic circuits for various purposes, including filtering, energy storage, and signal coupling.
C = Q / V
Where: C = Capacitance (F), Q = Charge (C), V = Voltage (V)
•If a capacitor stores 0.002 C of charge at 10 V: C = 0.002 / 10 = 0.0002 F (200 µF)
• If the charge is 0.001 C and voltage is 5 V: C = 0.001 / 5 = 0.0002 F (200 µF)
If the charge is 0.001 C and voltage is 5 V: C = 0.001 / 5 = 0.0002 F (200 µF)
- Measured in Farads
- Can be polarized or non-polarized
- Stores electrical charge
- Power supply filtering
- Signal coupling and decoupling
- Energy storage
- Check polarity– Electrolytic capacitors must be connected the right way, or they can explode.
- Discharge before touching – Capacitors can store charge after power is off.
- Respect voltage rating – Never exceed the rated voltage.
- Handle with care– Physical damage can cause failure.
- Avoid heat – High temperature shortens capacitor life.